Smartphones have become essential, marking a new era of technological progress and intense competition. At the centre of this battleground is the Great Patent War, exemplified by the 2012 legal clashes between industry giants like Apple and Samsung. These battles, fought in both courts and markets, emphasize the significance of design patents in safeguarding innovation and upholding brand identity.
This article explores the pivotal role of design patent in shaping industries, examining their importance and highlighting their influence on modern business practices.
The Significance of Design Patents
Design patents are more than just legal tools; they serve as the foundation for safeguarding the visual identity of products across various industries. By securing design patent protection, innovators shield their creations from imitation and assert ownership over the ornamental aspects of their designs. Unlike utility patents, which protect the functional aspects of an invention, design patents focus solely on its aesthetic appeal—making them the guardians of intellectual property in a visually-oriented world.
The enforcement power of design patents cannot be overstated. They act as potent weapons in legal battles, providing clear evidence of infringement and facilitating swift resolutions. Furthermore, design patents undergo a streamlined approval process, typically receiving clearance within 9 to 18 months, and offer extensive protection lasting 14 years without additional maintenance fees.
In litigation scenarios, design patent provides a distinct advantage. Their visual nature simplifies disputes over infringement, making it easier for juries to understand and make judgments. This simplicity underscores the importance of including design patents in one’s intellectual property portfolio, ensuring robust protection against imitators and strengthening brand distinctiveness.
Mastering the Art of Design Patent Searches
Conducting thorough design patent searches is a crucial step in securing intellectual property rights. These searches involve analyzing existing patents to ensure the uniqueness and novelty of a proposed design. Success in obtaining a design patent relies on demonstrating the distinctiveness of the design, which grants protection for 14 years from the filing date.
Design patents find applications in a wide range of industries, from furniture to communication equipment. However, differentiating between utility and design patents can pose a challenge for innovators. While utility patents protect the functionality of an entire product, design patents focus solely on its aesthetic aspects.
To conduct effective design patent searches, innovators can utilize various resources such as the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) website, Google Patent Search, or specialized paid search services like Simple Patents or Quick Patents. These tools enable thorough exploration of existing patents, helping innovators avoid unintentional infringement on others’ intellectual property rights. The cost of using one of these search tools ranges from approximately $175 to $300, depending on the complexity and services provided.
A Glimpse into the History of Design Patents
Traditionally, patents have primarily focused on utility patents, which protect inventions such as processes or products. However, design patents center around the ornamental design of commercial items and rely more on drawings than technical descriptions. Unlike utility patents, design patents typically have a single claim that directly refers to the drawings for protection.
In the United States, design patents provide exclusive legal protection for the visual attributes of an item, prioritizing decoration over utility. Although the first Patent Act was passed in 1790, it wasn’t until 1842 that US patent laws allowed for the patenting of ornamental designs. Interestingly, the first design patent, issued in 1842 to George Bruce, did not include any drawings.
In 2008, the U.S. Federal Circuit simplified the test for design patent infringement, making it easier to prove infringement based on substantial resemblance.
Past Patent Wars: A Look Back in Time
Patent disputes have a long history, dating back to instances such as the Wright brothers’ use of lawsuits to hinder competition in the aviation industry to protect their airplane invention, and Alexander Graham Bell’s 11-year dispute over the telephone patent, including a notable case against the Western Union.
In the digital age, patent wars intensified. In the 1980s, tech companies from the United States and Japan engaged in a patent war, leading businesses to engage in a “fight patent with patent” approach, which later gave way to the rise of patent trolling. The term “patent troll,” coined in the 1990s, refers to aggressive patent assertion for financial gain.
Throughout the 1990s and 2000s, various industries, including antivirus software and e-commerce, were embroiled in patent disputes. Notable conflicts include Amazon versus Barnes & Noble over “one-click ordering” and Sony versus Kodak over digital camera patents.
Over the past 15 years, patent litigation trends have been dynamic, frequently influenced by legislative, administrative, and judicial developments. From 2005 to a peak in 2011-2012, total patent litigation more than doubled.
However, despite the peak in the early 2010s, overall patent litigation has since decreased, with Non-Practicing Entities (NPEs) playing a significant role in these trends.
Apple-Samsung Patent War: A Timeline
The ongoing saga of the Apple-Samsung patent war has captivated boardrooms and made headlines. However, its origins can be traced back to January 4, 2007, just four days before the iconic iPhone’s debut. On this date, Apple filed a series of four design patents, claiming the fundamental shape and graphical user interface (GUI) of the iPhone. In June of the same year, an additional set of colour design patents covering 193 screenshots of various iPhone interfaces were filed.
Let’s explore the four crucial design patents initially filed:
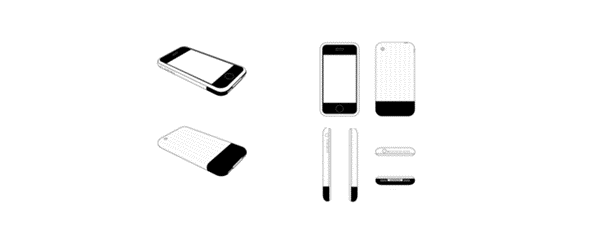
- D558757: This patent encapsulated the basic shape of the iPhone, a sleek, rounded-edge flat box, depicted in eight distinct views.
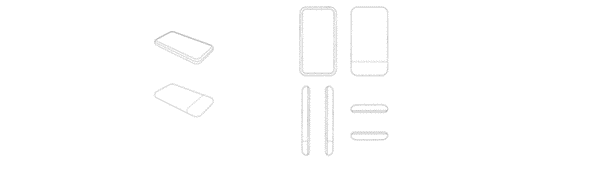
- D558756: This patent depicted various integral components like connectors, screens, and buttons, providing eight comprehensive views of the device.
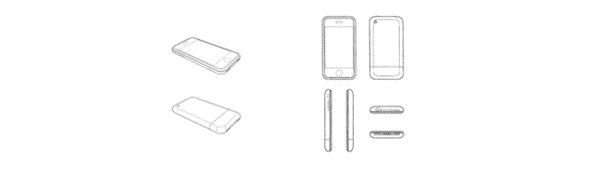
- D580387: This patent highlighted the surface finish, particularly the glass-like texture, with eight detailed views.
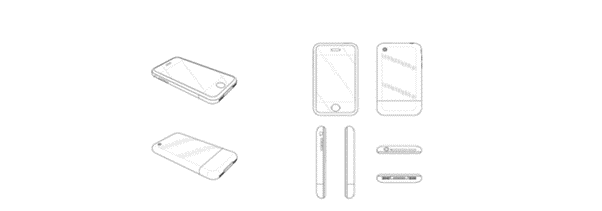
- D558758: Centered on the device’s color aspect, including variations like black and silver, this patent also showcased eight detailed views.
The legal dispute between Apple and Samsung began when Samsung started distributing Android handsets, leading Steve Jobs, the then CEO of Apple, to famously refer to it as a “stolen” product—a knockoff of the iPhone. Here’s a timeline of the ensuing battle:
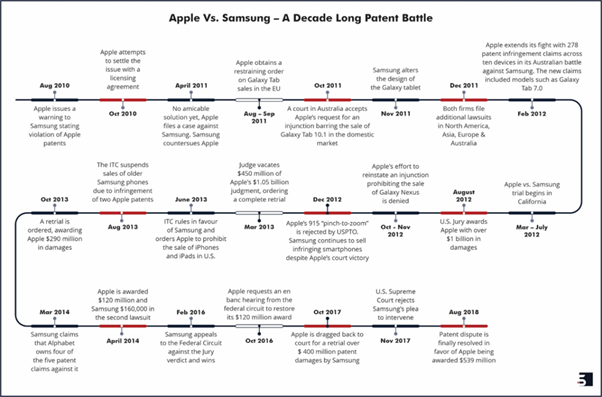
So, who emerged as the winner in this battle?
Both Apple and Samsung were found guilty of infringing on each other’s patents during the patent trial. While Samsung was not initially required to pay the $1 billion in damages, it did suffer a significant setback. Apple, which was also found guilty of duplicating several of Samsung’s patents, vehemently argued that the penalty was excessive. This case highlights the importance of protecting and enforcing design patents to avoid substantial financial losses and brand dilution.
The Influence of Smartphone Patent Wars on the Electronics & Communication Industry
The smartphone patent wars had a profound impact on the electronics and communication industry, leading to a re-evaluation of product design strategies. The industry was compelled to reassess its approach due to the high costs of litigation and significant court awards. Minor design modifications that were previously sufficient for product launches became impractical. As a result, there has been a notable increase in design patent registrations since 2011, as depicted in the accompanying charts.
How Patent Wars Impacted Annual Patent Trends
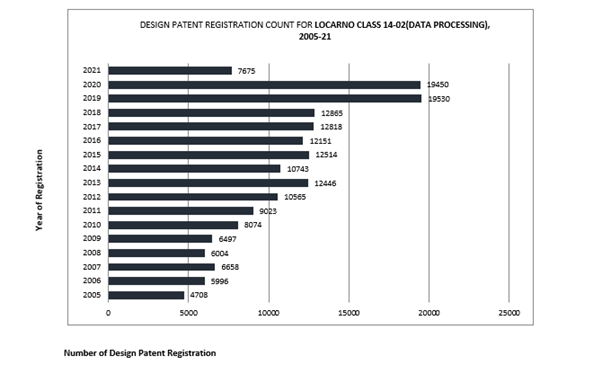
The graph depicts a significant increase in design registrations from 2011 (9023) to 2019 (19530), reflecting over 100% growth. Notably, two patents in litigation, D504889 and D618677, fall under the 14-02 Locarno Classification, indicating substantial development in data processing devices.
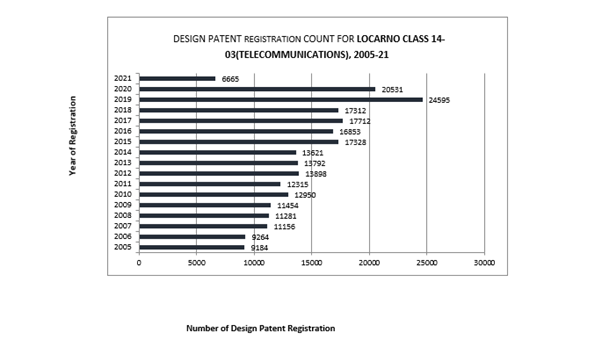
There’s a clear upward trend from 2011 (12315) to 2019 (24595), nearly doubling in growth. One of the patents in litigation, D593087, belongs to the 14-03 Locarno Classification, suggesting significant innovation in telecommunications devices.
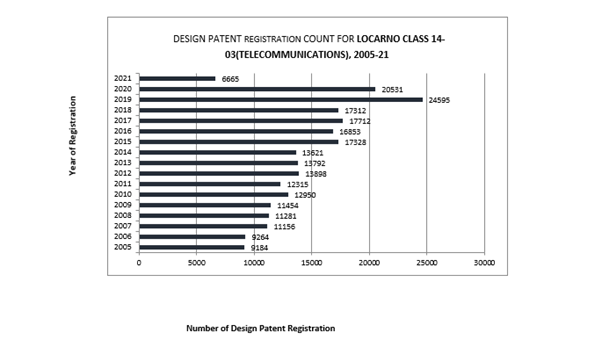
There’s a clear upward trend from 2011 (12315) to 2019 (24595), nearly doubling in growth. One of the patents in litigation, D593087, belongs to the 14-03 Locarno Classification, suggesting significant innovation in telecommunications devices.
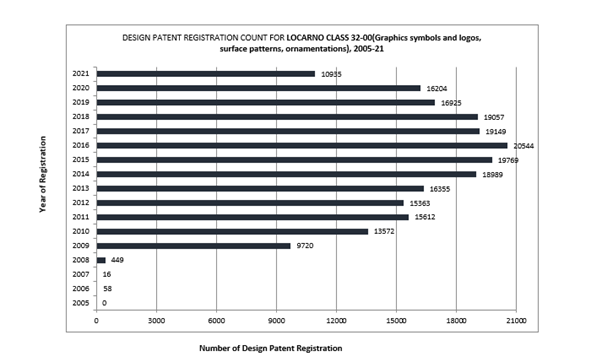
While there was an upward trend from 2011 to 2016, a subsequent decline by 2020 erased the gains made during the growth period.
Impact of Patent Wars on Annual Patent Trends
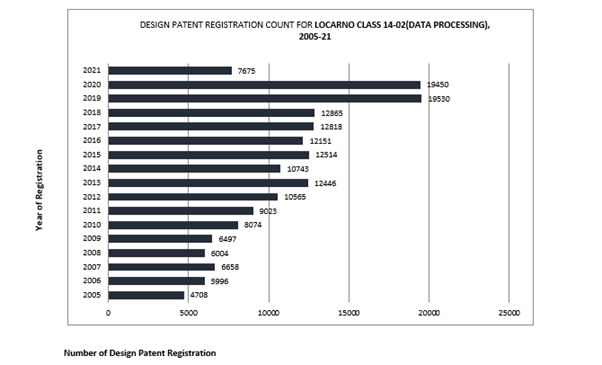
The graph illustrates a significant growth in design registrations from 2011 (9023) to 2019 (19530), representing a growth rate of over 100%. Notably, two patents involved in litigation, D504889 and D618677, fall under the 14-02 Locarno Classification, indicating substantial advancements in data processing devices.
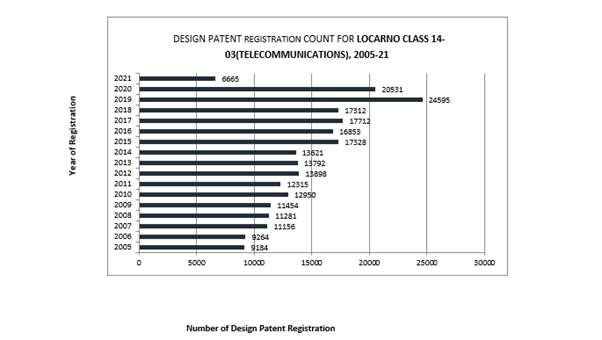
There is a clear upward trend from 2011 (12315) to 2019 (24595), nearly doubling in growth. One of the patents in litigation, D593087, belongs to the 14-03 Locarno Classification, suggesting significant innovation in telecommunications devices.
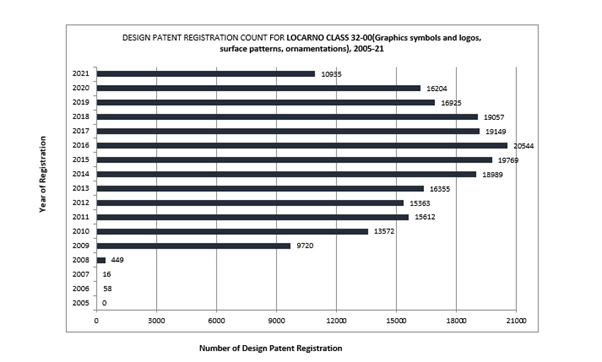
While there was an upward trend from 2011 to 2016, subsequent decline by 2020 erased the gains made during the growth period.
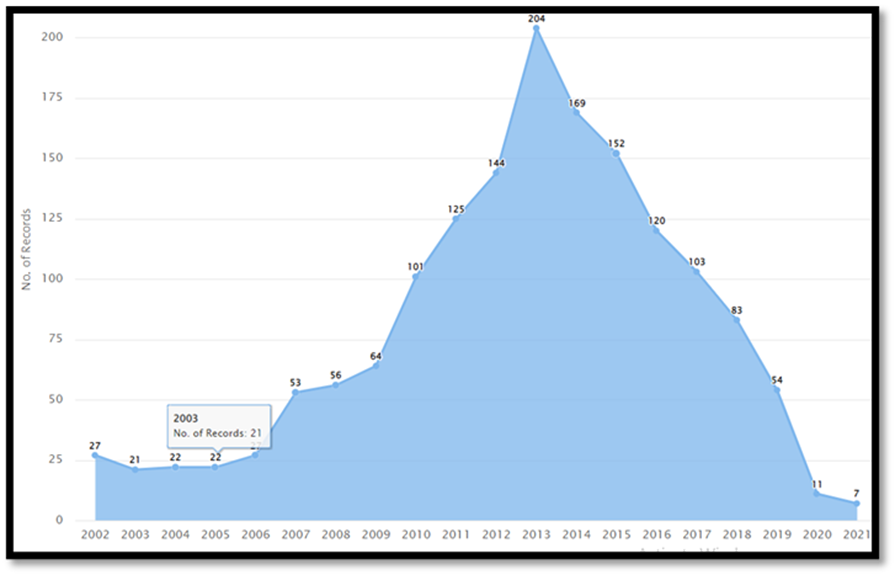
From Figure 9, it is evident that the count of design patent records (US Class D14/341, for design patent number D504889) showed an upward trend from 2002 to 2013, with the record count increasing from twenty-seven to two hundred and four. However, from 2013 onwards, the count has consistently declined, reaching a low of eleven records in 2020.
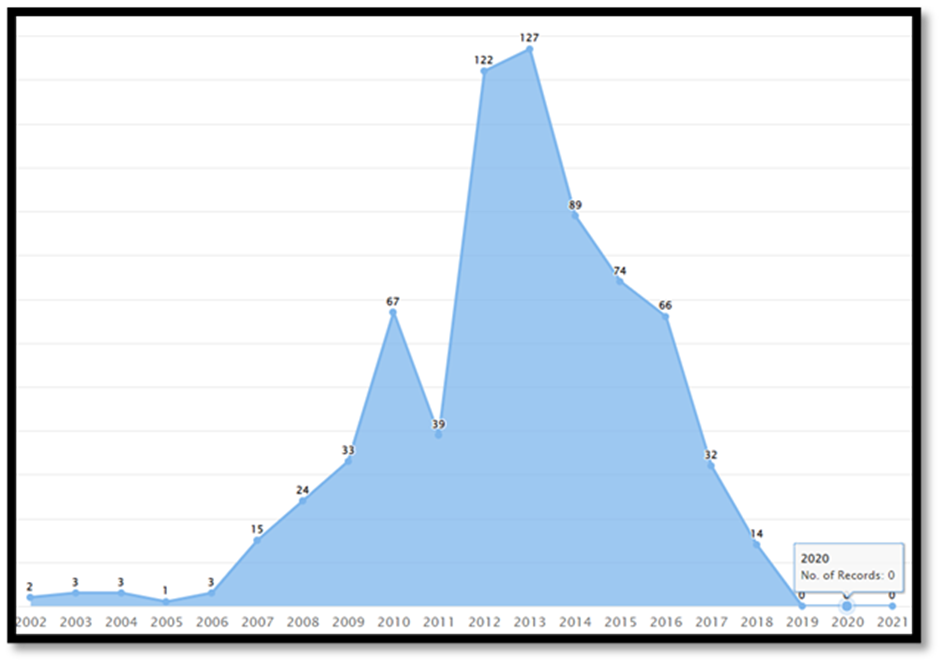
From Figure 10, it is apparent that the count of design patent records (US Class D14/138G, for design patent number D593087) showed an upward trend from 2006 to 2010, with the record count increasing from three to sixty-seven. After a dip in 2011, the count increased again, reaching a peak of 127 in 2013. However, since 2013, the count of design patent records has consistently declined.
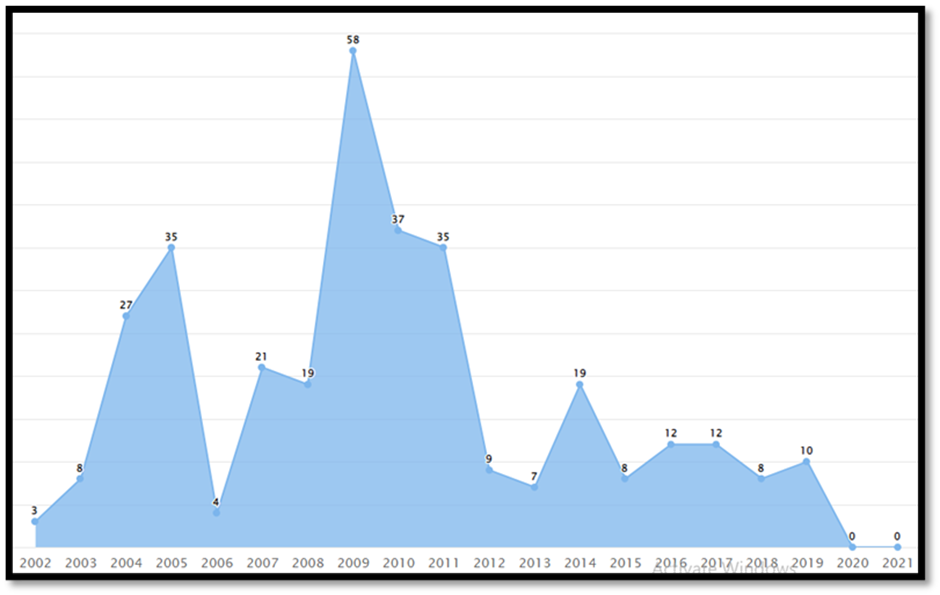
From Figure 11, we can observe that the count of design patent records (US Class D14/203.7, for design patent number D593087) showed an upward trend from 2002 to 2005, with the record count increasing from three to thirty-five. After a dip in 2006, the count increased again, reaching a maximum of 58 in 2009. Since then, there has been inconsistency in the count of design patent records.
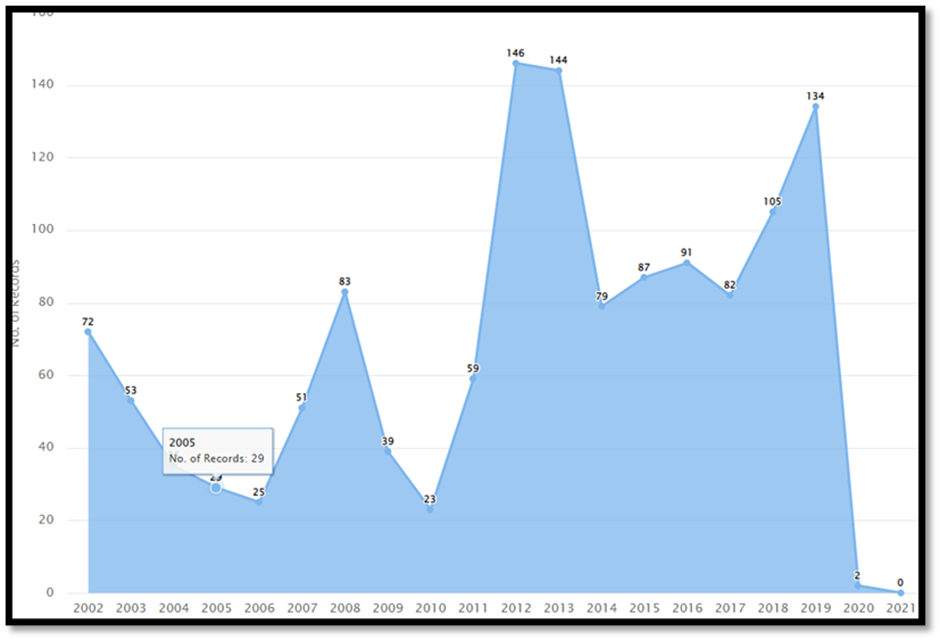
Figure 12 shows that the count of design patent records (US Class D14/248, for design patent number D618677) demonstrated an upward trend from 2010 to 2012, with the record count increasing from twenty-three to one hundred and forty-six. The count increased again from 2017 to 2019, rising from eighty-two to one hundred and thirty-four.
Understanding these design patent trends, both within Locarno and US classes, provides insight into the evolving landscape of innovation and intellectual property protection within the electronics and communication industry.
Why should design searches be a fundamental component of your business strategy?
Industrial design significantly contributes to the commercial value and market appeal of a product by making it more visually appealing to consumers. Protecting an industrial design ensures a reasonable return on investment in its creation.
Industrial designs enhance the aesthetics and attractiveness of a product, influencing consumer choices and purchase decisions. The appearance of a product plays a significant role in consumer preferences. Therefore, industrial design is crucial for businesses of all sizes, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and larger corporations, across various industries.
Industrial design is essential for developing products that meet user demands and aspirations while differentiating them from competitors. However, many businesses fail to fully grasp the benefits of design due to a lack of technical knowledge and challenges in integrating industrial design into the product development process. Those who understand and incorporate design searches into their management strategy can fully capitalize on the advantages.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, design patents play a central role in protecting and preserving innovation, particularly in our visually oriented world. They not only provide robust protection against imitation but also enhance brand distinctiveness and competitive advantage. The Apple-Samsung patent war serves as a clear example of the significance of design patents, showcasing their influence on industries and business practices. Therefore, conducting comprehensive design patent searches and understanding their enforcement should be strategic priorities for businesses. Ultimately, in the competitive realm of innovation, design patents act as powerful shields, safeguarding creative brilliance and fortifying market positions.
PatSketch offers a Design Patent Search service tailored to address the aesthetic aspects of inventions, empowering businesses and inventors to effectively identify relevant prior art and potential infringements. Our expert team navigates through relevant design classifications and term sets to formulate a comprehensive search strategy. To learn more about our design patent services, click here.
